Clean, filtered water for better living
Taste the In-Store difference. Our water solutions use multiple stages of filtration to deliver expertly treated water from source to tap.

Did you know?
Bottle water can cost up to
10,000 TIMES MORE than tap water.
Torontonians consume an estimated 100 million plastic bottles annually, and 35% are not recycled.
All tap water contains millions of impurities, including many that you can’t taste, see or smell.
Why choose In-Store Water Systems?
- Canadian-owned & operated
- 30+ years in business
- NSF-certified products
- Unbeatable quality, service and price

Learn more about In-Store Water Systems
Products
Our products
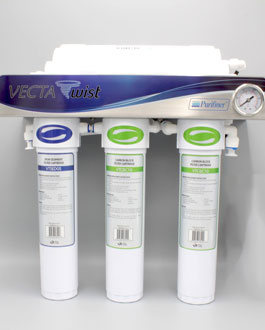
Premier Series

Optimum Series

Iron Filter

Signature Series

UV

Accessories – Leak Detection
Sign up for a free water analysis
Superior drinking water for you and your family

Clean
Control your water quality and experience fresh, filtered water.

Affordable
Enjoy an unlimited supply of clean water at a fraction of the cost of bottled water.
Convenient
Experience clean water at your fingertips with easy installation and no heavy bottles to lift.

Trusted by our valued partners:





Testimonials
The water is so crisp! We’ve been coming for years. Efficient self-serve service and helpful staff when I needed some assistance.
— A English
I have been buying water from In-Store Water Systems for as long as I can remember. The staff has always been friendly and provided great customer service.
— S Fairman
Clean install. No issues. Everything works great, and we’re enjoying the new system.
— B D’Souza
I have been a long-time customer of In-Store Water Systems and think this business is wonderful.
— S Biagioni
The quality of the In-Store Water Systems water-softener systems and RO drinking water systems are excellent.
— S Adamo
The refilling stations are conveniently located and are very well kept. The staff are friendly and accommodating.
— R Padua
I highly recommend In-Store Water Systems for their professionalism, friendly staff and prompt after-sales service.
— D Malcolm
In-Store Water Systems has always provided us with prompt, dependable customer service from the day they installed our system right through our annual servicing.
— N Biagioni
I have been a loyal customer of In-Store Water Systems for years now, and they never disappoint.
— T Ngo
Booking the appointment was easy. The installer was great and did a fantastic job. The system is running beautifully. Highly recommend In-Store Water Systems. A++
— B Smith
Their refilling system is convenient and easy, and they also have great pricing compared to other brands.
— C Dibuja
My system has really helped me with my skin problems, especially in the summer and winter.
— N Kasarr
My water has never tasted better. Good customer service with knowledgeable staff.
— S Murray
I’ve been going to In-Store Water Systems for almost 15 years, and their service has always been great.
— S Lochner
Customer service is fantastic. Always so pleasant and helpful. Love our reverse osmosis water system and soft water system!
— T Kalsi
Years of great customer service and delicious water. I come down every week from my place just to buy their water. I highly recommend this place.
— A Sadat
Family owned company with a focus on quality water at an affordable price, combined with great customer service.
— N Bourne
Great water. Very convenient filling stations. Love using the dolphin water pump they sell.
— R Goebel
Great water and extensive filtration process! Definitely recommend!
— B Bajnauth
Love their water filtration system! I have been drinking their water for years!
— D Jeyakumar
Great service. Love coming here!
— E Ozabor
Very knowledgeable staff. I will definitely be back at this store.
— D Newman
We have had their water system for years now and cannot imagine having anything else.
— S Nikolov
Amazing service and been with them for over 10 years.
— J Frangella
Awesome staff and great service. I would recommend them to anyone.
— A Guido
This is where I’ve been getting my family’s drinking water for the past 10 years.
— M Galloway




